COMP 303 - Lecture Notes for Week 7 - Java Object Model
- Slides edited from, Object-Oriented Design Patterns, by
Cay S. Horstmann
- Original slides available from:
http://www.horstmann.com/design_and_patterns.html
- Modifications made by Laurie Hendren, McGill University
- Topics this week:
- The Java Type System
- Type Inquiry
- The Object Class
- Shallow and Deep Copy
- Serialization
- Reflection
- The Java Beans Component Model
Types
- Type: set of values and the operations that can be applied to the
values
- Strongly typed language: compiler and run-time system check that no
operation can execute that violates type system rules
- Compile-time check
Employee e = new
Employee();
e.clear(); // ERROR
- Run-time check:
e = null;
e.setSalary(20000); // ERROR
Java Types and Values
Types
- Primitive types:
int short long byte
char float double boolean
- Class types
- Interface types
- Array types
- The null type
- Note: void is not a type
Java Values
- value of primitive type
- reference to object of class type
- reference to array
- null
- Note: Can't have value of interface type
Subtype Relationship
S is a subtype of T if
- S and T are the same type
- S and T are both class types, and T is a direct or indirect
superclass of S
- S is a class type, T is an interface type, and S or one of its
superclasses implements T
- S and T are both interface types, and T is a direct or indirect
superinterface of S
- S and T are both array types, and the component type of S is a
subtype of the component type of T
- S is not a primitive type and T is the type Object
- S is an array type and T is Cloneable or Serializable
- S is the null type and T is not a primitive type
The ArrayStoreException
Wrapper Classes
Enumerated Types
- Finite set of values
- Example: { SMALL,
MEDIUM, LARGE }
- Java has no syntax for enumerated types
- Can fake them with integer constants
public static final int SMALL =
1;
public static final int MEDIUM = 2;
public static final int LARGE = 3;
- Not typesafe
int size =
LARGE;
size++;
Typesafe Enumerations
Type Inquiry
- Test whether e is a Shape:
if (e instanceof Shape) . . .
- Common before casts:
Shape s = (Shape) e;
- Don't know exact type of e
- Could be any class implementing Shape
- If e is null, test returns false (no exception)
The Class Class
- getClass method gets class of any object
- Returns object of type Class:
-
Class object describes a type
Object e = new Rectangle();
Class c = e.getClass();
System.out.println(c.getName()); // prints java.awt.Rectangle
- Class.forName method yields Class object:
Class c = Class.forName(java.awt.Rectangle);
- .class suffix yields Class object:
Class c = Rectangle.class; // java.awt prefix not needed
- Class is a misnomer: int.class,
void.class,Shape.class
An Employee Object vs.
the Employee.class
Object
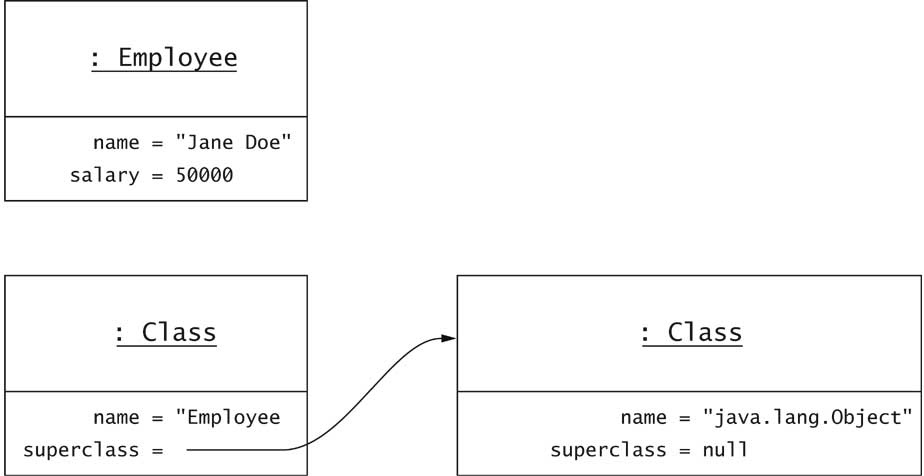
Type Inquiry
- Test whether e is a Rectangle:
if (e.getClass() == Rectangle.class) . . .
- Ok to use ==
- A unique Class object for every class
- Test fails for subclasses
- Use instanceof to test for subtypes:
if (x instanceof Rectangle) . . .
Array Types
Object: The Cosmic Superclass
- All classes extend Object
- Most useful methods:
- String toString()
- boolean equals(Object otherObject)
- Object clone()
- int hashCode()
The toString Method
- Returns a string representation of the object
- Useful for debugging
- Example: Rectangle.toString returns something like
java.awt.Rectangle[x=5,y=10,width=20,height=30]
- toString used by concatenation operator
- aString + anObject
means
aString + anObject.toString()
- Object.toString prints class name and object address
System.out.println(System.out)
yields
java.io.PrintStream@d2460bf
- Implementor of PrintStream didn't override
toString:
Overriding the toString Method
- Format all fields:
public class Employee
{
public String toString()
{
return getClass().getName()
+ "[name=" + name
+ ",salary=" + salary
+ "]";
}
...
}
- Typical string:
Employee[name=Harry Hacker,salary=35000]
Overriding toString in Subclass
- Format superclass first
public class Manager extends Employee
{
public String toString()
{
return super.toString()
+ "[department=" + department + "]";
}
...
}
- Typical string
Manager[name=Dolly Dollar,salary=100000][department=Finance]
- Note that superclass reports actual class name
The equals Method
- equals tests for equal contents
- == tests for equal location
- Used in many standard library methods
- Example: ArrayList.indexOf
/**
Searches for the first occurrence of the given argument,
testing for equality using the equals method.
@param elem an object.
@return the index of the first occurrence
of the argument in this list; returns -1 if
the object is not found.
*/
public int indexOf(Object elem)
{
if (elem == null)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elementData[i] == null) return i;
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elem.equals(elementData[i])) return i;
}
return -1;
}
Overriding the equals Method
Overriding equals in Subclass
Not all equals Methods are Simple
The Object.equalsMethod
Requirements for equals Method
- reflexive: x.equals(x)
- symmetric: x.equals(y) if and only if
y.equals(x)
- transitive: if x.equals(y) and
y.equals(z), then x.equals(z)
- x.equals(null) must return false
Fixing Employee.equals
- Violates two rules
- Add test for null:
if (otherObject == null) return false
- What happens if otherObject not an Employee
- Should return false (because of symmetry)
- Common error: use of instanceof
if (!(otherObject instanceof Employee)) return false;
// don't do this for non-final classes
- Violates symmetry: Suppose e, m have same name,
salary
e.equals(m) is true (because m instanceof
Employee)
m.equals(e) is false (because e isn't an
instance of Manager)
- Remedy: Test for class equality
if (getClass() != otherObject.getClass()) return
false;
The Perfect equals Method
Hashing
- hashCode method used in HashMap,
HashSet
- Computes an int from
an object
- Example: hash code of String
int h = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++)
h = 31 * h + s.charAt(i);
- Hash code of "eat" is
100184
- Hash code of "tea" is
114704
Hashing
Shallow and Deep Copy
- Assignment (copy = e) makes shallow copy
- Clone to make deep copy
- Employee cloned = (Employee)e.clone();
Cloning
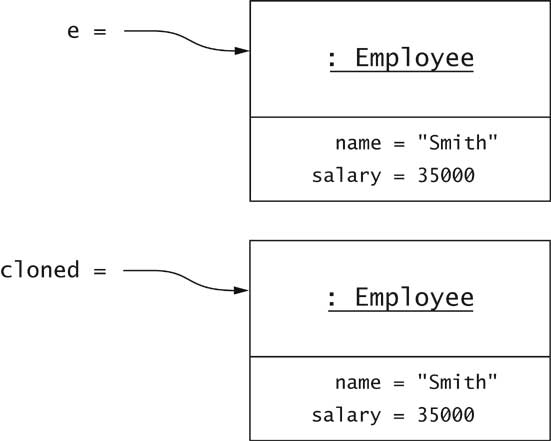
Cloning
The Cloneable Interface
The clone Method
public class Employee
implements Cloneable
{
public Object clone()
{
try
{
return super.clone();
}
catch(CloneNotSupportedException e)
{
return null; // won't happen
}
}
...
}
Shallow Cloning
- clone makes a shallow copy
- Instance fields aren't cloned
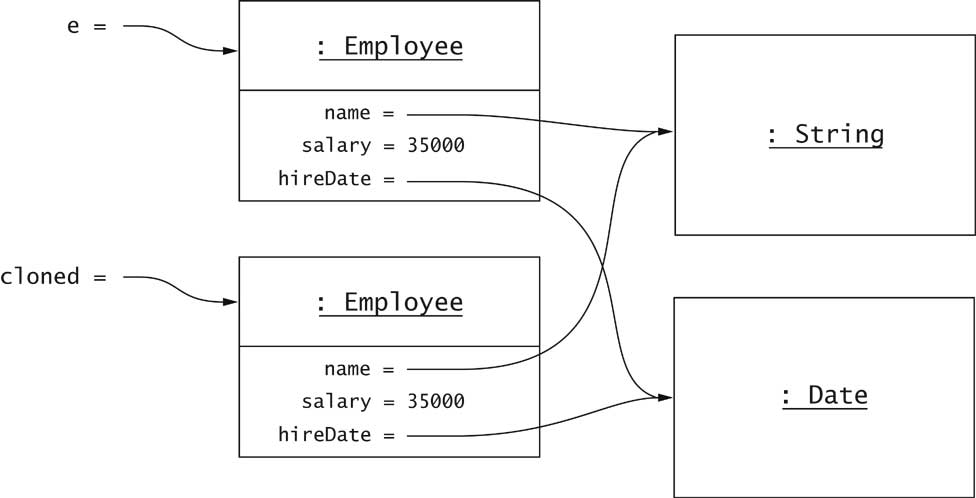
Deep Cloning
- Why doesn't clone make a deep copy?
Wouldn't work for cyclic data structures
- Not a problem for immutable fields
- You must clone mutable fields
public class Employee
implements Cloneable
{
public Object clone()
{
try
{
Employee cloned = (Employee)super.clone();
cloned.hireDate = (Date)hiredate.clone();
return cloned;
}
catch(CloneNotSupportedException e)
{
return null; // won't happen
}
}
...
}
Deep Cloning
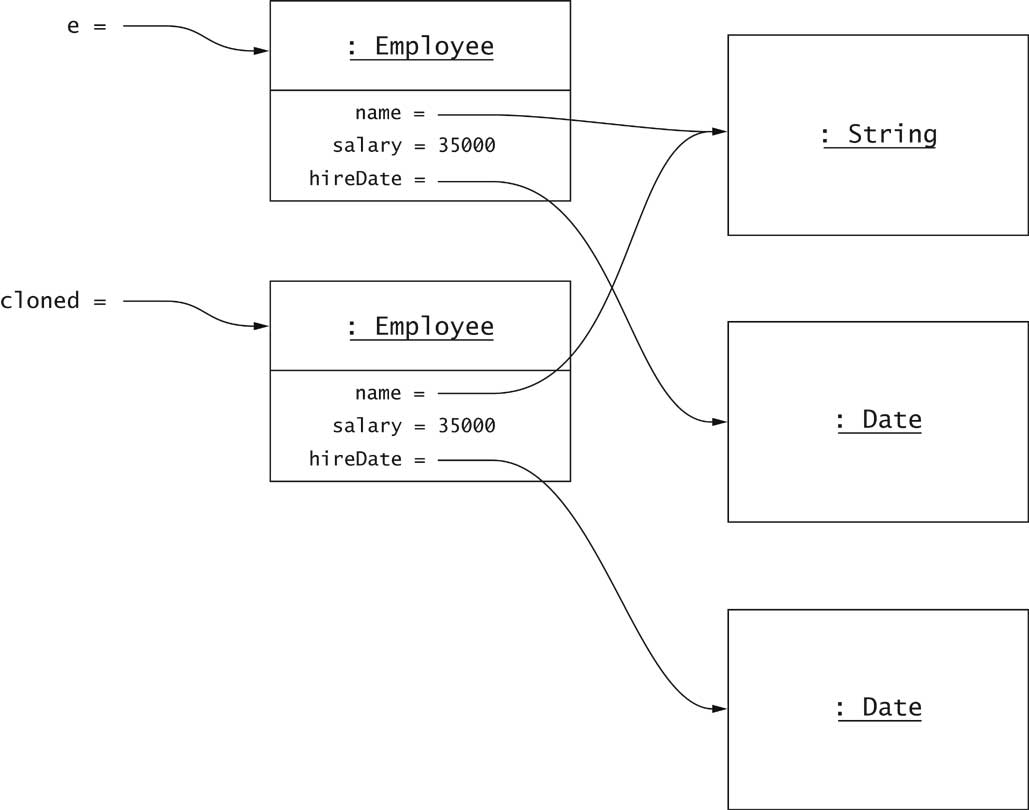
Cloning and Inheritance
- Object.clone is paranoid
- clone is protected
- clone only clones Cloneable objects
- clone throws checked exception
- You don't have that luxury
- Manager.clone must be defined if Manager
adds mutable fields
- Rule of thumb: if you extend a class that defines clone,
redefine clone
- Lesson to learn: Tagging interfaces are inherited. Use them only to
tag properties that inherit
Serialization
- Save collection of objects to stream
Employee[] staff = new Employee[2];
staff.add(new Employee(...));
staff.add(new Employee(...));
- Construct ObjectOutputStream:
ObjectOutputStream out
= new ObjectOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream("staff.dat"));
- Save the array and close the stream
out.writeObject(staff);
out.close();
Serialization
- The array and all of its objects and their dependent objects
are saved
- Employee doesn't have to define any method
- Needs to implement the Serializable interface
- Another tagging interface with no methods
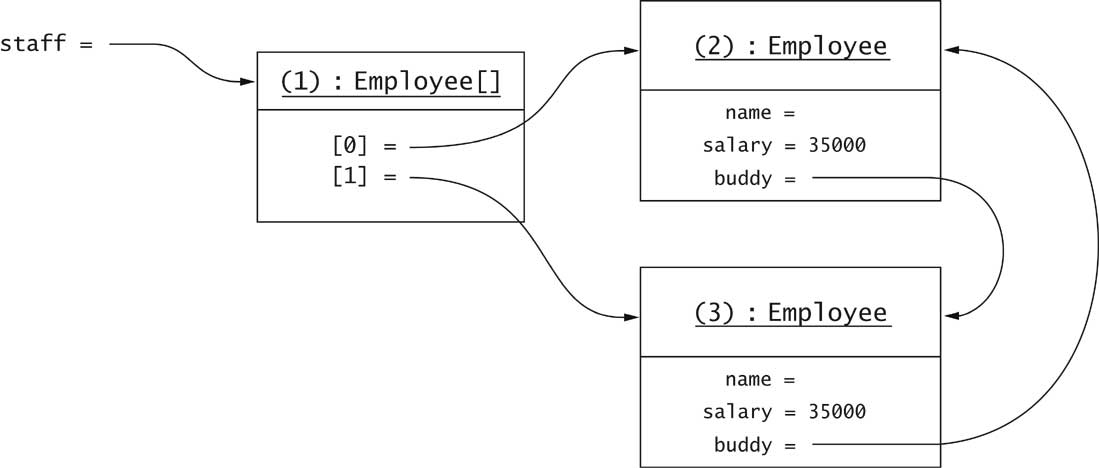
How Serialization Works
- Each newly encountered object is saved
- Each object gets a serial number in the stream
- No object is saved twice
- Reference to already encountered object saved as "reference to
#"
Serializing Unserializable Classes
- Some classes are not serializable
- Security? Anonymous classes? Programmer cluelessness?
- Example: Ellipse2D.Double
- How can we serialize Car?
- Suppress default serialization to avoid exception
- Mark with transient:
private transient Ellipse2D frontTire;
- Supply private (!) methods
private void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream out)
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream in)
- In these methods
-
- Call
writeDefaultObject/readDefaultObject
- Manually save other data
- Ch7/serial/Car.java
Reflection
- Ability of running program to find out about its objects and
classes
- Class object reveals
- superclass
- interfaces
- package
- names and types of fields
- names, parameter types, return types of methods
- parameter types of constructors
Reflection
- Class getSuperclass()
- Class[] getInterfaces()
- Package getPackage()
- Field[] getDeclaredFields()
- Constructor[] getDeclaredConstructors()
- Method[] getDeclaredMethods()
Example: Enumerating static fields Math class
Field[] fields = Math.class.getDeclaredFields();
for (int i = 0; i < fields.length; i++)
if (Modifier.isStatic(fields[i].getModifiers()))
System.out.println(fields[i].getName());
Enumerating Constructors
- Print the names and parameter types of all Rectangle
constructors:
for (int i = 0; i < cons.length; i++)
{
Class[] params = cons[i].getParameterTypes();
System.out.print("Rectangle(");
for (int j = 0; j < params.length; j++)
{
if (j > 0) System.out.print(", ");
System.out.print(params[j].getName());
}
System.out.println(")");
}
- Yields
Rectangle()
Rectangle(java.awt.Rectangle)
Rectangle(int, int, int, int)
Rectangle(int, int)
Rectangle(java.awt.Point, java.awt.Dimension)
Rectangle(java.awt.Point)
Rectangle(java.awt.Dimension)
Getting A Single Method Descriptor
- Supply method name
- Supply array of parameter types
- Example: Get Rectangle.contains(int, int):
Method m = Rectangle.class.getDeclaredMethod(
"contains",
new Class[] { int.class, int.class });
- Example: Get default Rectangle constructor:
Constructor c = Rectangle.class.getDeclaredConstructor(
new Class[] {});
Invoking a Method
- Supply implicit parameter (null for static
methods)
- Supply array of explicit parameter values
- Wrap primitive types
- Unwrap primitive return value
- Example: Call System.out.println("Hello, World") the hard
way.
Method m = PrintStream.class.getDeclaredMethod(
"println",
new Class[] { String.class } );
m.invoke(System.out,
new Object[] { "Hello, World!" });
Inspecting Objects
- Can obtain object contents at runtime
- Useful for generic debugging tools
- Need to gain access to private fields
Class c = obj.getClass();
Field f = c.getDeclaredField(name);
f.setAccessible(true);
- Throws exception if security manager disallows access
- Access field value:
Object value = f.get(obj);
f.set(obj, value);
- Use wrappers for primitive types
Inspecting Objects
- Example: Peek inside string tokenizer
- Ch7/code/reflect2/FieldTest.java
- Output
int currentPosition=0
int newPosition=-1
int maxPosition=13
java.lang.String str=Hello, World!
java.lang.String delimiters=,
boolean retDelims=false
boolean delimsChanged=false
char maxDelimChar=,
---
int currentPosition=5
. . .
Inspecting Array Elements
- Use static methods of Array class
Object value = Array.get(a, i);
Array.set(a, i, value);
int n = Array.getLength(a);
- Construct new array:
Object a = Array.newInstance(type, length);
Components
- More functionality than a single class
- Reuse and customize in multiple contexts
- "Plug components together" to form applications
- Successful model: Visual Basic controls
- Examples:
- calendar
- graph
- database
- link to robot or instrument
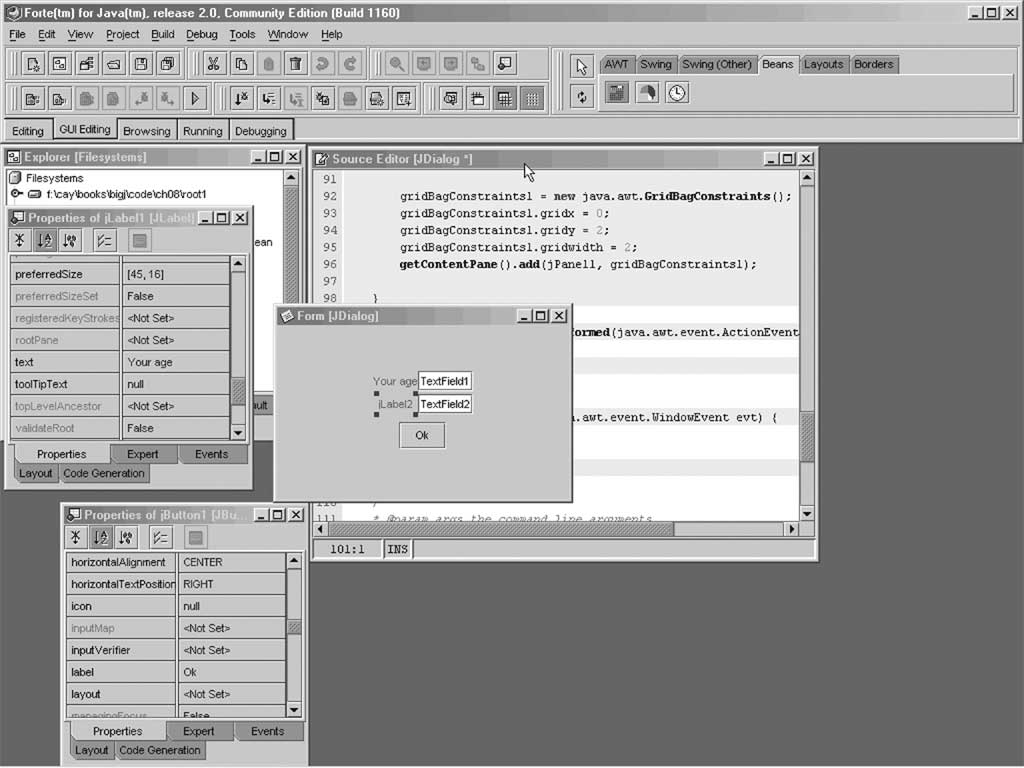
- Components composed into program inside builder environment
A Builder Environment
Java Beans
- Java component model
- Bean has:
- methods (just like classes)
- properties
- events
A Calendar Bean
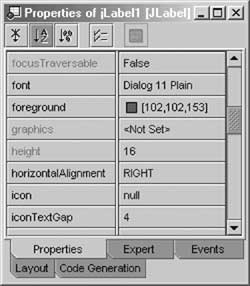
A Property Sheet
- Edit properties with property sheet
Facade Class
- Bean usually composed of multiple classes
- One class nominated as facade class
- Clients use only facade class methods
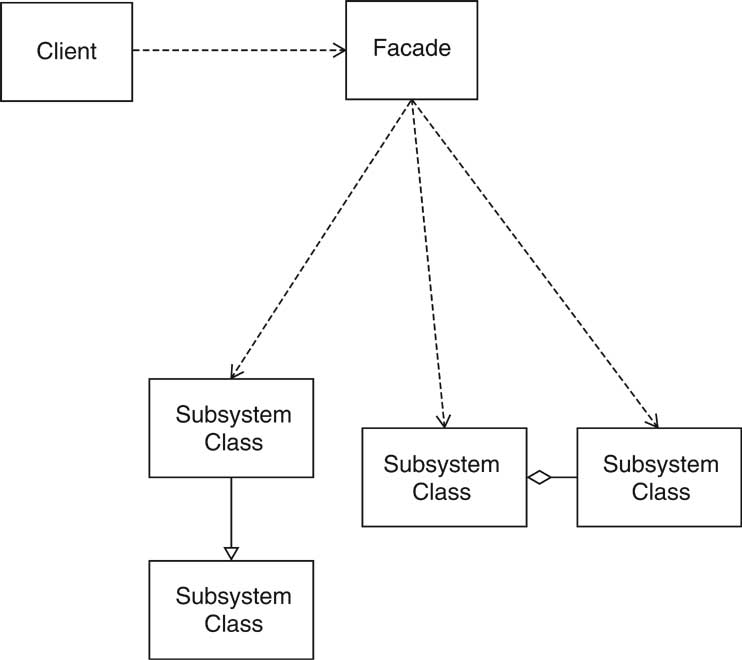
Facade Pattern
Context
- A subsystem consists of multiple classes, making it complicated for
clients to use
- Implementor may want to change subsystem classes
- Want to give a coherent entry point
Solution
- Define a facade class that exposes all capabilities of the
subsystem as methods
- The facade methods delegate requests to the subsystem classes
- The subsystem classes do not know about the facade class
Facade Pattern
Facade Pattern
Name in Design
Pattern
|
Actual Name
(Beans)
|
Client
|
Builder tool
|
Facade
|
Main bean class with which the
tool interacts
|
SubsystemClass
|
Class used to implement bean
functionality |
Bean Properties
- Property = value that you can get and/or set
- Most properties are get-and-set
- Can also have get-only and set-only
- Property not the same as instance field
- Setter can set fields, then call repaint
- Getter can query database
Property Syntax
- Not Java :-(
- C#, JavaScript, Visual Basic
- b.propertyName =
value
calls setter
- variable = b.propertyName
calls getter
Java Naming Conventions
- property = pair of methods
public X getPropertyName()
public void setPropertyName(X newValue)
- Replace propertyName with actual name
(e.g. getColor/setColor)
- Exception for boolean properties:
public boolean isPropertyName()
- Decapitalization hokus-pokus:
getColor -> color
getURL -> URL
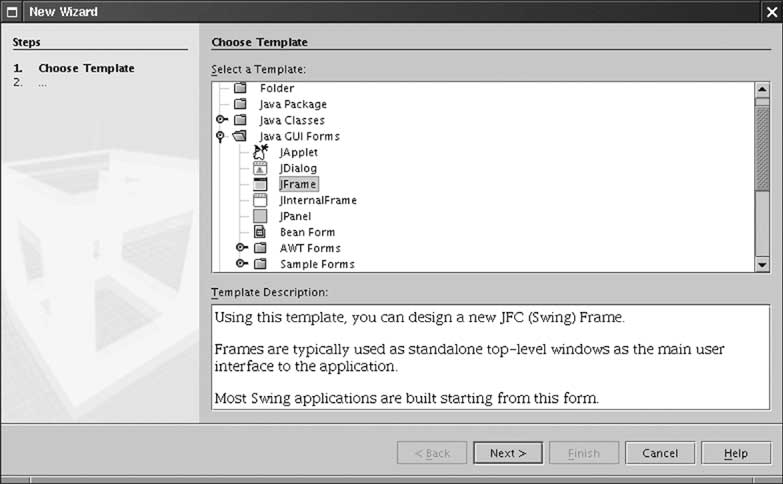
Editing Beans in a Builder Tool
- Use wizard to make empty frame
Editing Beans in a Builder Tool
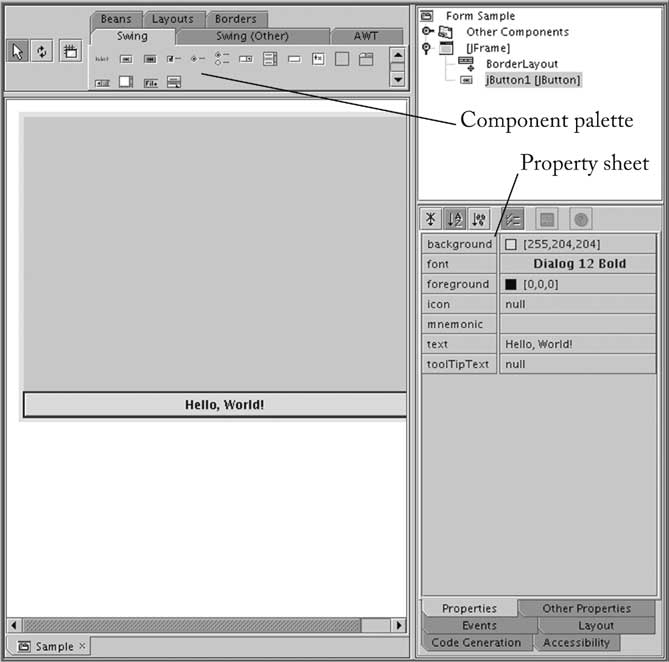
- Add button to frame, then edit button with property sheet.
Packaging a Bean
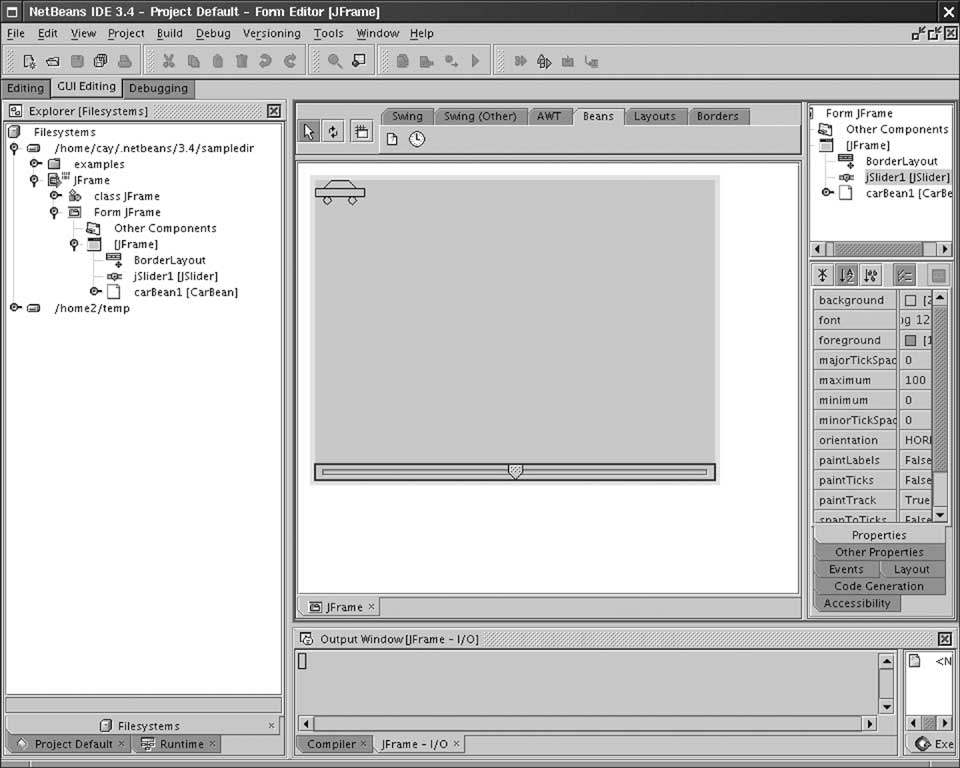
Composing Beans
- Make new frame
- Add car bean, slider to frame
- Edit stateChanged
event of slider
- Add handler code
carBean1.setX(jSlider1.getValue());
- Compile and run
- Move slider: the car moves
Bean Information
- Builder environment loads beans
- Looks for get/set methods in facade class
- Can discover spurious properties
JButton: Object getTreeLock()
- Alternate mechanism: BeanInfo class
- Must have name FacadeClassNameBeanInfo
- E.g. HouseBeanBeanInfo
The BeanInfo Interface
Image getIcon(int iconKind)
BeanDescriptor getBeanDescriptor()
MethodDescriptor[] getMethodDescriptors()
PropertyDescriptor[] getPropertyDescriptors()
EventSetDescriptor[] getEventSetDescriptors()
int getDefaultEventIndex()
int getDefaultPropertyIndex()
BeanInfo[] getAdditionalBeanInfo()
Removing Spurious Properties
class MyBeanBeanInfo extends SimpleBeanInfo
{
public PropertyDescriptor[] getPropertyDescriptors()
{
try
{
return new PropertyDescriptor[]
{
new PropertyDescriptor("x", CarBean.class);
new PropertyDescriptor("y", CarBean.class);
};
}
catch (IntrospectionException exception)
{ return null; }
}
}
Property Editors
- Property sheet enumerates properties
- Allows user to edit property values
- How can one edit values of arbitrary types?
- Built-in editors for String, Color, etc
- Supply custom editor for your own types
Custom Property Editors
- Three kinds of editors
- Text
- Finite set of choices
- Arbitrary painting and editing
- Implement PropertyEditor interface
- Or extend PropertyEditorSupport class
Editing Text Properties
Editing Choice Properties
- Your type has finite set of string choices
- E.g. DrawMode.DRAW, DrawMode.FILL
- String[] getTags() returns array of choices
- Also need to define getAsText/setAsText
- Property sheet uses combo box
Editing Arbitrary Properties
- Your type isn't easily editable as string
- E.g. Color
- Property editor pops up your edit dialog
- boolean supportsCustomEditor() must return
true
- Component getCustomEditor() returns
dialog
- Property editor can paint current value of your type
- boolean isPaintable() must return true
- void paintValue(Graphics g, Rectangle bounds)
paints
Registering Property Editors
- Global setting
PropertyEditorManager.registerEditor(valueClass, editorClass)
- Per-bean setting
In bean info class:
PropertyDescriptor dimensionProperty = new PropertyDescriptor(
"dimension", CarBean.class);
dimensionProperty.setPropertyEditorClass(DimensionEditor.class);
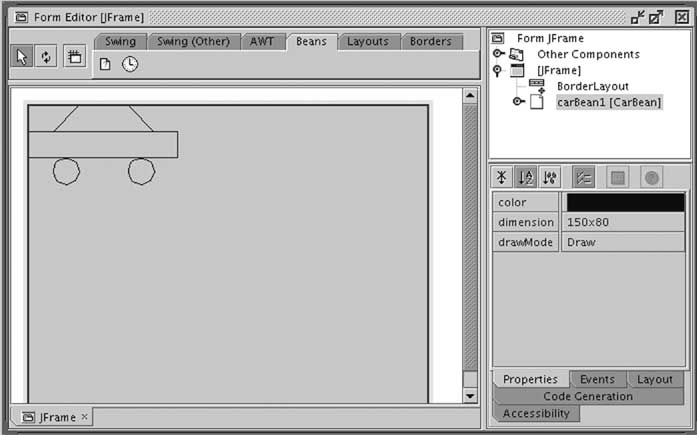
Example: CarBean
Example: CarBean
Implementing a Property Sheet
- Used for graph framework in chapter 8
- Form shows property names on left, editors on right
Implementing a Property Sheet
- Get bean info for class
- Get properties from bean info
- Obtain property getter/setter methods from property descriptor
- Use these methods to read and write property values
- Each editor is text field, combo box, or button with painted
icon
- Clicking on button brings up dialog
- Ch7/propedit/PropertySheet.java
- Ch7/propedit/PropertySheetTest.java















